 |
 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Aiming for Regenerating Articular Cartilage with Hydrostatic Pressure |
Takashi Ushida, Prof., School of Medicine (concurrent with Department of Mechanical Engineering) As the great age society is going, osteoarthritis, disease of joint cartilage getting worn out, is increasing. Cartilage plays an important role on joint movement. When cartilage gets worn out bones hit each other to get inside nerves stimulated, causing severe pains. Eventually the patients are getting difficult to walk, resulting in low quality of life (QOL). Among the people who have past middle age, osteoarthritis is detected frequently. As one of the treatments in regenerative medicine, transplantation of chondrocytes, cells in cartilage has been tried. However, its efficiency is still low. We have been trying to regenerate cartilage tissue itself for transplanting it to damaged portion of articular joints. How to proliferate cultured chondrocytes efficiently. How to regenerate articular cartilage tissue. (1) biochemical methods by using growth factors such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF), (2) methods in material engineering by using bio-degradable polymers such as poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA). We have adopted a third method, method in mechanics, by using physical stimulations, which are thought to be physiologically loaded with. Articular cartilage is thought to be physiologically loaded with hydrostatic pressure up to 50 atm, corresponding to water pressure at 500 m in depth, by weight and exercise. Cartilage is composed of 10 % in matrices and 90 % in water, then compressive stress is transiently transformed to hydrostatic pressure inside cartilage tissue. We think such a physical condition controls cellular functions and promotes tissue regeneration. Actually we have achieved to make cartilage tissue elements under hydrostatic pressure loading. However, there still remains much work to seek for adequate loading conditions of hydrostatic pressure. How does chondrocyte sense hydrostatic pressure? We have studying its sensing mechanism by detecting intracellular signals evoked by hydrostatic pressure. In the future, we hope that articular cartilage can be regenerated in a tailor-made manner, so that the shape of regenerated cartilage can be regulated by using a mould made by rapid prototyping method, based on X-CT 3D data. |
I was brought up in a region where a huge automobile company reigned. I had relative some of whom founded companies relating to automobile. So I was thinking I would also do so. However when I met a research theme on artificial kidney at the graduate school, I clearly understood that medical engineering was that I sought for, though it was a little late. So when I entered Agency of Industrial Science & Technology (present National Institute Of Advanced Industrial Science & Technology), I started culturing mammalian cells in the laboratory. It was a turning point for me that I started the cell culture and made biomedical researches under Professor Tateishi, who is one of the founders of biomechanics in Japan. Collaboration between medicine and engineering, has been defined to collaboration between medical doctors and engineers. I think that this definition is already out of date. I think that researchers with basement of the both engineering and medical in themselves are required for future progress in medical engineering field. In that sense, I want that the students should have wishes to exploit new fields on the base of their disciplines. My hobby is listening to classical music at outdoor, using a iPod with a noise-cancelled headphone. I remember that I have played trombone at a citizen orchestra. I like looking outside from the train windows. Away from the daily works, ideas or hint to solve difficult problems might unexpectedly come up to me. I don't hesitate to take a train, although the destination may be at a flight distance. I highly value such precious time. |
|
Effect of physiological hydrostatic pressure on regeneration of cartilage tissue elements 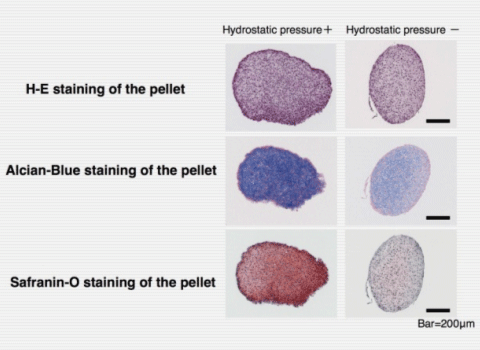 The images show histochemical staining of cartilage tissue elements under hydrostatic pressure loading or not. Haematoxylin-Eosin staining shows cell viability and distribution. On the other hand, both Alcian-Blue staining and Safranin- O staining show the matrices of cartilage, such as chondroitin sulfate, heparan sulfate. The images show that hydrostatic pressure loading promoted the regeneration of cartilage tissue elements. |

<Personal Background> 1979:graduated from Faculty of Eng., Univ. of Tokyo, 1980:studied at School of Med, Nancy Univ., France, 85: graduated from Graduate School of Eng. Univ. of Tokyo. Ph.D. 1985: researcher at Agency of Industrial Science and Technology. 1992:conjugated associate prof., School of Med., Tsukuba Univ. 2000:associate prof., Faculty of Eng., Univ. of Tokyo. 2003:prof., Center for disease biology and Integrative Medicine, School of Med., Univ. of Tokyo, concurrent to Dep of Mech Eng., Faculty of Eng., Univ. of Tokyo. |
| <<Back | Page top |